DTVM
Smart Contract Overview
Jovay adopts the DTVM virtual machine as the execution engine for smart contracts. At its core, it is a WebAssembly JIT virtual machine, but it provides compatibility with the EVM contract ecosystem, including the ability to use the same contract ABI as EVM for contract deployment and invocation, and support for common SDKs and clients such as web3js, web3j, and MetaMask. For contract developers, it supports Solidity-compatible contract syntax and common contract frameworks like Foundry for contract development and compilation. Additionally, it supports other traditional programming languages such as C++ (currently available), Rust, Java, Go, and AssemblyScript (TypeScript subset) (being gradually introduced) for smart contract development. These contracts can interoperate with Solidity contracts and can be called using common SDKs and clients like web3 and MetaMask.
DTVM Introduction
DTVM (DeTerministic Virtual Machine) is a next-generation blockchain virtual machine that addresses critical performance, determinism, and ecosystem compatibility challenges in blockchain networks. Building upon WebAssembly (Wasm) while maintaining full Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) ABI compatibility. 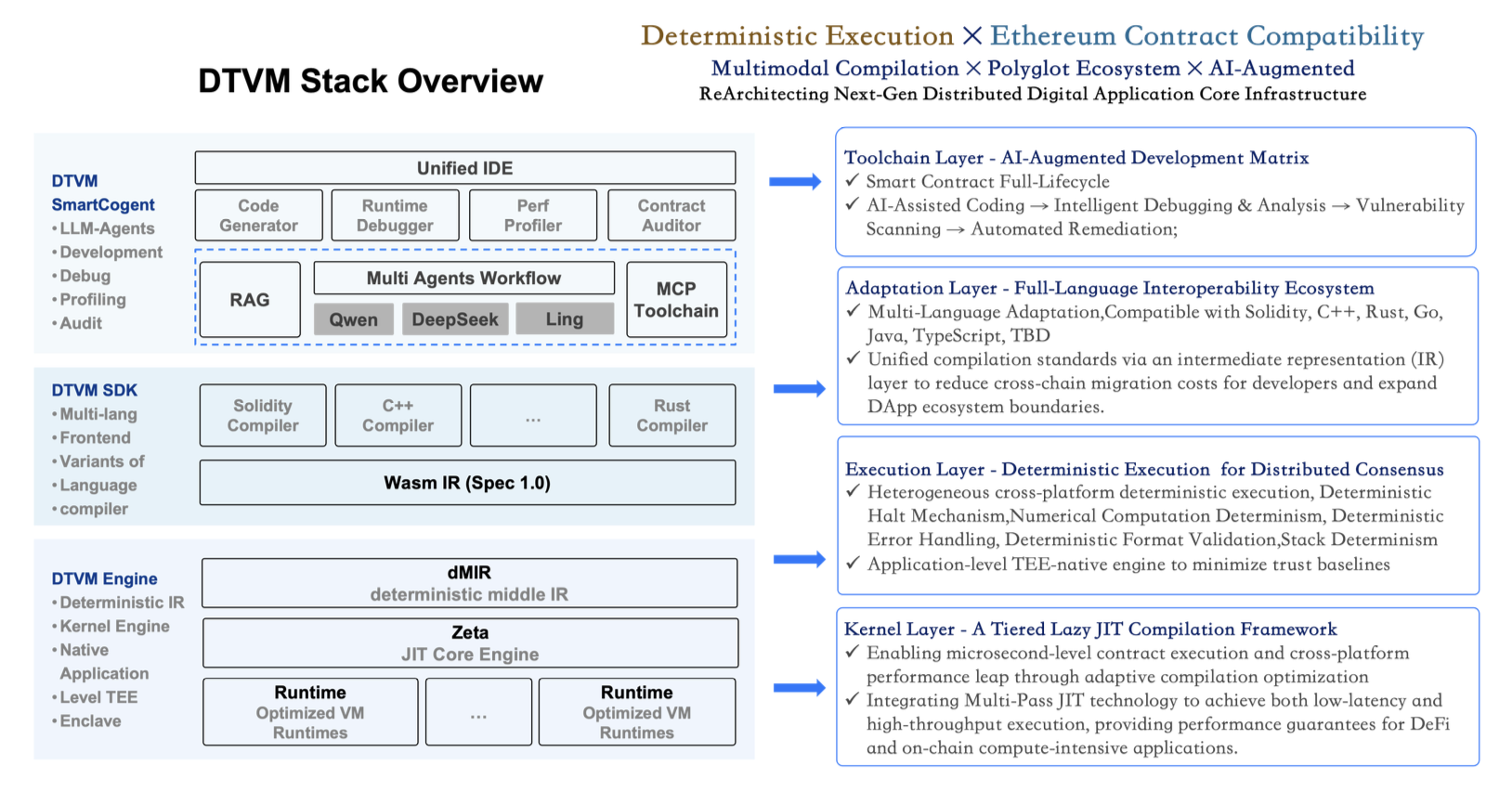
You can read the DTVM technical paper for more details: https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.16552
DTVM introduces:
1. Deterministic JIT Execution Engine with Enhanced Performance
Central to the DTVM Stack is an ultra-fast execution engine that employs deterministic JIT compilation. This engine implements a unique function-level lazy JIT compilation framework, which enables asynchronous compilation at the granularity of individual functions. To address the inherent trade-off between compilation time and execution performance in traditional JIT processes, DTVM introduces a hybrid compilation strategy, which dynamically adapts and switches between O0 and O2 compilation optimization levels during runtime, thereby optimizing both compilation efficiency and execution speed. Additionally, the DTVM Stack proposes Deterministic Middle Intermediate Representation (dMIR), a blockchain-specific intermediate representation that ensures deterministic execution guarantees. By carefully analyzing non-deterministic behaviors in Wasm runtime, DTVM identifies three major categories of non-determinism: Static and loading-time non-determinism, Runtime non-determinism and Exception and trap non-determinism. To eliminate these non-determinism, DTVM propose several novel mechanisms: Deterministic Halt Mechanism, Numerical Computation Determinism, Deterministic Error Handling, Deterministic Format Validation and Stack Determinism. These mechanisms collectively ensure predictable and strict deterministic execution outcomes.
2. EVM ABI Compatibility and Multi-Language Ecosystem Support
The DTVM Stack maintains compatibility with the latest Solidity 0.8.x specification while expanding support to six frontend programming languages (e.g. Solidity, C/C++, Rust, Java, Golang, and AssemblyScript). The unified contract bytecode intermediate representation enables efficient conversion between EVM bytecode and other language-specific formats. Benefiting from these designs, DTVM Stack facilitates cross-language interoperability, enabling seamless coordination between different contract implementations and enhancing the flexibility of smart contract engineering.
3. TEE-Native Security and Hardware-Optimized Efficiency
For application-level TEEs such as Intel SGX, the DTVM Stack offers high portability through a minimized Trusted Computing Base (TCB). Compared to competitive Wasm implementations, the DTVM Stack reduces codebase size to 48% (comparing to Wasmtime) and binary library size to approximately 60%, thereby minimizing potential attack surfaces while maintaining security and efficiency. Additionally, the framework leverages modern processor registers and exception handling mechanisms to address specialized requirements such as gas metering and boundary checks in JIT compilation. This design effectively balances security and performance by ensuring efficient resource utilization without compromising execution safety.
4. SmartCogent: AI-Powered Smart Contract Development and Auditing
SmartCogent is developed based on a multi-agent architecture. It automates critical stages of the smart contract lifecycle, including code generation, compilation, testing, deployment, and security auditing. Leveraging advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) data and Large Language Model (LLM) capabilities, it enhances the developer experience by introducing intelligent automation into the development process.
Significant advantages are demonstrated by DTVM in deterministic smart contract execution efficiency, post-deployment invocation latency, multi-language ecosystem support, and intelligent development through comprehensive benchmarking.
1). Superior Deterministic Execution Efficiency:
Performance improvements of up to 2× are achieved in dominant Ethereum ERCs (e.g. ERC20/721/1155) contract execution compared to evmone, with a 3.61× acceleration observed for compute-intensive Fibonacci workloads. The JIT compilation mode further delivers a 58.54× performance gain over the interpreter baseline. When evaluated against mainstream Wasm VMs, the framework exhibits an average speedup ratio of 1.20∼12.14× across the PolyBench standard bench suite, while reducing Fibonacci processing time by 11.8∼40.5%, with cross-architecture deterministic execution guarantee in all tested scenarios.
2). Sub-Millisecond Post-Deployment Invocation Latency: The on-demand compilation mechanism reduces the post-deployment invocation time to 0.95ms in PolyBench cases, achieving over 23× speedup compared to Wasmtime (Cranelift as JIT backend). This rapid invocation capability is critical for blockchain transaction processing, as prolonged loading times can induce notable performance degradation and expose exploitable vulnerabilities for DDoS attacks.
3). Enhanced Functionality with Full Compatibility: In code generation metrics, machine code object sizes are reduced by 30∼72% relative to comparable solutions, with the core codebase (69.5KLoC) representing only 48% of Wasmtime’s implementation. The CLI binary footprint (32MB) is minimized by up to 71% compared to baseline systems, establishing a minimized Trusted Computing Base (TCB) for secure execution environments. Functional validation confirms DTVM’s dual capability of maintaining full Ethereum ecosystem compatibility while establishing a multi-language smart contract development framework supporting C/C++, Rust, Java, Go, and AssemblyScript.
4). Intelligent Coding and High-precision Security Auditing: DTVM’s integrated SmartCogent delivers an 81% accuracy rate in vulnerability detection and an 86% success rate in automated repair, significantly surpassing other baseline models and specialized tools. These extensive experimental results highlight the DTVM Stack as an efficient and secure infrastructure execution framework for high-performance blockchain applications, providing optimized computational throughput with deterministic execution guarantees.
DTVM SDK
DTVM’s adaptation layer supports multi-language contract development, providing frontend design capabilities for contracts written in Solidity, C++, Rust, Go, Java, AssemblyScript, and more. It includes SDKs with diverse template libraries to streamline development. The core objective is to offer developers a high-efficiency, user-friendly, and multi-language environment that seamlessly integrates with the underlying DTVM engine. By providing language-specific SDKs, developers can select the most suitable language based on project requirements, team expertise, or language advantages (e.g., Rust’s security, C++’s performance, or Solidity’s Ethereum compatibility), thereby lowering barriers to entry for the DTVM ecosystem and enabling the creation of complex, high-performance decentralized applications.
Key features include:
For each supported programming language, we provide a dedicated Software Development Kit (SDK). These SDKs are designed not just as simple interface wrappers but come equipped with comprehensive functionalities to enhance developers’ experience when working with the DTVM engine. Core Features of the SDKs Include:
Runtime Libraries: Comprehensive APIs that allow interaction with fundamental DTVM engine capabilities. This includes:
State Management, Functions for reading from and writing to contract storage, such as simulating Solidity’s mapping and state variables.
Context Access, Easy retrieval of transaction data like sender address (msg.sender) and value (msg.value), along with block information including timestamps and block numbers.
Event Triggering, Standardized interfaces for emitting events, facilitating off-chain applications to monitor these events effectively.
Host API Invocation, Encapsulated interfaces for calling deterministic Host functions of the DTVM, streamlining complex operations.
ABI Encoding/Decoding,Tools to process function parameters and return values according to standard interface specifications, ensuring seamless communication between contracts.
Build Tool Integration: The SDKs include plugins or scripts tailored for integration with language-specific build tools such as Maven or Foundry. This integration simplifies the workflow from compiling, optimizing, to packaging source code into executable Wasm bytecode for the DTVM, enhancing development efficiency. We also provide thorough documentation aimed at guiding developers through the installation and usage of our SDKs, alongside deep dives into core API concepts. To further accelerate onboarding and facilitate understanding, extensive example codes are available, demonstrating practical implementations and best practices.
This approach ensures that developers have all the necessary resources at their disposal to efficiently develop, test, and deploy applications on the DTVM platform.
DTVM Compatibility with EVM
DTVM currently supports the EVM ecosystem through EVM ABI compatibility, Solidity 0.8 syntax compatibility, and SDK and client compatibility. Developers can use the original Solidity syntax and Foundry framework to develop smart contracts, use DTVM's contract language SDK to compile to Wasm bytecode, and then use Ethereum community's web3 sdk to deploy to the blockchain and call contracts. This provides a compatible experience for both developers and users.
For contract developers, in addition to facilitating the migration of existing contracts and the use of existing contract libraries through Solidity syntax compatibility, for computation-intensive smart contracts such as cryptography or those requiring calls to existing C++, Rust, Java, and other language code, developers can use these Web3 programming languages to develop contracts. They can compile to Wasm contract bytecode using DTVM's SDK and deploy to the blockchain. Users can call these contracts just like Solidity contracts, and they can even be called by other Solidity contracts. While maintaining compatibility in user experience and ecosystem, this provides developers with more options.
DTVM Solidity Language Support
DTVM's first contract language support is for Solidity, with its open-source repository available on GitHub at https://github.com/DTVMStack/DTVM_SolSDK.
DTVM_SolSDK serves as a valuable tool for compiling Ethereum Solidity smart contracts into WebAssembly (Wasm), thereby facilitating their deployment on Wasm-based blockchains. Currently, DTVM_SolSDK supports Solidity 0.8 syntax and integrates with the Foundry framework for contract development. To begin writing your first Solidity contract on DTVM, please consult the documentation here: https://github.com/DTVMStack/DTVM_SolSDK/blob/main/docs/release_docs/quick-start.md.
To ensure compatibility with the EVM, DTVM_SolSDK employs a process where Solidity contracts are first compiled into Yul assembly language using a Solidity compiler, and then these Yul contracts are transcompiled into Wasm bytecode.
DTVM C++ Language Support
DTVM offers support for writing WebAssembly contracts using C++/C, while maintaining compatibility with the EVM ABI.
The DTVM C++ contract SDK is open-sourced and available on GitHub at https://github.com/DTVMStack/DTVM_CppSDK.
When using DTVM_CppSDK to write C++ contracts, you can define contract interfaces, methods, events, and storage using the Solidity language. The DTVM_CppSDK will then generate corresponding C++ header files from the Solidity code, allowing developers to implement the abstract methods defined in Solidity using C++.
A key advantage of DTVM_CppSDK is the ability to develop computationally intensive contracts with EVM ABI compatibility. You can leverage C++ contracts to implement complex computational logic, such as cryptographic operations or intricate formulas, and then invoke these C++ contracts from your Solidity contracts.
For more information, please refer to the documentation available at https://github.com/DTVMStack/DTVM_CppSDK/tree/main/docs.