Jovay - A High Performance Dual-Prover Layer 2
Abstract
The advent of Web3 has unleashed a wave of innovation. However, the industry still faces critical bottlenecks that impede its path to mainstream adoption. To unlock its full potential and enable large scale adoption, future Web3 innovation will center on bridging the physical and digital worlds, particularly through the crypto economy represented by Real World Assets (RWA). The convergence between the physical and digital, Web2 and Web3, TradFi and DeFi, will drive substantial growth in the global crypto economy. This vision forms the foundation of Jovay. Jovay is a cutting-edge Layer 2 that delivers superior performance in throughput and latency while addressing crucial security challenges. It remains fully compatible with Ethereum ecosystem. Its core architecture combines a heterogeneous dual-prover mechanism with fully pipelined parallel execution, delivering 100,000+TPS and 100ms confirmation latency with Layer 1 level security, resolving key issues such as congestion, high gas fees, and poor user experience. By leveraging smart contract Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation and the VEPT verifiable computing paradigm, Jovay supports advanced use cases such as on-chain AI model execution, expanding blockchain's application boundaries. With Jovay, developers can build high throughput DApps efficiently using its AI-powered full stack toolchain, while users enjoy near-centralized responsiveness. Jovay aims to serve as the trusted infrastructure for the global RWA token economy in the AI era, bridging value and consensus between Web2 and Web3.
1.Why do we need Jovay?
The Importance of RWA for Web2: Throughout financial history, the ultimate goal has been the optimal allocation of capital and assets. This requires standardized platforms and processes for asset issuance and trading, improved credit mechanisms, and reduced issuance and transaction costs. Among emerging solutions, tokenization stands out as the most effective tool for addressing these requirements. RWA token economies can accelerate asset data standardization, tokenization of ownership, enhance liquidity and global accessibility, thereby infusing new vitality into the growth of the global economy.
The Importance of RWA for Web3: A pivotal bottleneck within the contemporary Web3 ecosystem lies in its highly financialized and insular characteristics, which lack a genuine anchoring to real-world value. This closed-loop system risks engendering a circular flow of finance devoid of substantive value and hinders broader participation. A sustainable RWA ecosystem has the potential to introduce dependable, external value into Web3, integrate with advanced decentralized technologies, and attract wider user and capital engagement. Consequently, this fosters healthier and more sustainable long-term development.
The Role of AI in the Future of RWA: AI is poised to play a crucial role in reshaping RWA, spanning from asset creation to the establishment of value consensus and market formation. AI-powered services have the potential to generate new asset classes that yield sustainable value and cash flows, thereby necessitating the development of new financial infrastructures. The establishment of consensus on asset value demands data that is comprehensive, verifiable, and timely. Traditional assets already present challenges due to their fragmented nature. AI-generated assets will further amplify these complexities. Addressing these issues requires more sophisticated AI tools. Moreover, AI-enhanced information collection, trading decisions, and automated execution, when integrated with on-chain RWAs and programmable logic, will markedly enhance transactional efficiency and market security. These applications elevate the requirements for AI's trustworthiness, reliability, and verifiability. Consequently, the advancement of AI technologies becomes imperative for overcoming existing challenges and unlocking new potentials within the RWA ecosystem.
Why Jovay Matters for the RWA Economy: The subsequent phase of the RWA token economy necessitates an enhanced financial infrastructure. As a component of Ant Digital Technologies' "Dual Chains and One Bridge" RWA solution, Jovay functions as the transaction chain. It provides Ethereum-compatible Layer 2 scalability characterized by high throughput, low latency, and rapid confirmation. This integration encompasses several key innovations: fully pipelined parallel execution, lazy Just-In-Time (JIT) smart contract compilation, random aggregation-based SumCheck ZK proofs, heterogeneous hardware acceleration, and the VEPT verifiable computing paradigm.
Leveraging the VEPT framework, Jovay provides AI-friendly compute extensions that extend the capabilities of Layer 1 applications. It supports full-stack AI-assisted contract development, encompassing tools for debugging, performance tuning, and security auditing. Serving as a bridge between Web2 and Web3, Jovay is dedicated to open collaboration, seamlessly integrating with Layer 1 and Layer 2 chains, compliant exchanges, DeFi protocols, and on-chain compliance standards (KYC/AML). This integration facilitates multi-party co-construction and all-win cooperation, laying a robust foundation for the sustainable evolution of RWA enhanced by AI.
| Anchor Trust with Data and AI | Embrace Developer Experience | Bridge Assets, Interchain Liquidity | Tokenize Assets, Converge Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Table 1: Jovay's Business Objectives
In this white paper, we will discuss Jovay's core design concept, key technical architecture, and novel application development paradigm.
2.Design Principles
Considering Jovay's core positioning and current technological trends, the following principles guided our Layer 2 system design:
- Heterogeneous Proof Systems for Security Resilience: To avoid systemic vulnerabilities inherent in single-prover systems, Jovay employs a dual-prover architecture combining ZK and TEE, enabling cross verification of execution results. This design addresses both latency sensitivity in RWA scenarios and foundational security requirements. The approach is conceptually aligned with the tri-prover scheme proposed by Buterin [1], which emphasizes confirmation based on agreement across at least two proof types.
- End-to-End Scalability in Throughput: Scalability is addressed holistically, covering transaction processing, proof generation, and intermediate data preparation (e.g., Trace data). For RWA use cases with highly variable workloads, the system needs to maintain relatively stable throughput under dynamic scenarios.
- Real-Time Responsiveness for Web2 Integration: As an intermediary between traditional financial systems and Web3 infrastructure, Jovay must meet real-time performance standards comparable to those of conventional finance, ensuring seamless interoperability in latency-sensitive RWA applications.
- Compatibility with the AI Ecosystem: With the emergence of LLMs and intelligent services, the system is designed to support verifiable computation and interoperability with AI ecosystems, enabling applications such as AI-assisted development, trading, and analytics. This capability is critical to expanding Web3's interface with intelligent automation.
3.Technical Overview
Jovay is a next-generation Layer 2 network designed for the future Web3 ecosystem. With native compatibility to the Ethereum ecosystem, Jovay addresses blockchain performance bottlenecks and alleviates the constraints of the "blockchain trilemma." By leveraging a heterogeneous dual-prover architecture and implementing comprehensive technological innovations, Jovay achieves high throughput, low latency, and rapid finality, redefining the scalability boundaries of Layer 2.
While maintaining interoperability with Ethereum, Jovay introduces innovative techniques that substantially improve computing, storage, and proof efficiency. Overall, Jovay provides a unified infrastructure that harmonizes security, scalability, and usability for both developers and end users.
3.1.Core Architecture and Performance Breakthrough
During the transaction execution phase, Jovay achieves full process parallelization of computation and I/O by integrating several key techniques. These include fully pipelined execution, lazy Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation for smart contracts, highly-parallelized transaction execution engine, and batched data access mechanism. This architectural design breaks down transaction processing into multiple independent execution units and maximizes the utilization of hardware resources through a dynamic load balancing mechanism. Consequently, Jovay is capable of delivering performance exceeding 100,000 transactions per second (TPS) on a single chain, with confirmation latency under 100 milliseconds.
Simultaneously, Jovay employs a heterogeneous dual-prover architecture, combining a random aggregation-based SumCheck zero-knowledge proof algorithm with heterogeneous hardware acceleration techniques. These innovations significantly enhance the efficiency of proof generation and verification, substantially reducing the costs associated with proof production and on-chain verification.
3.2.Three-Stage Confirmation Mechanism
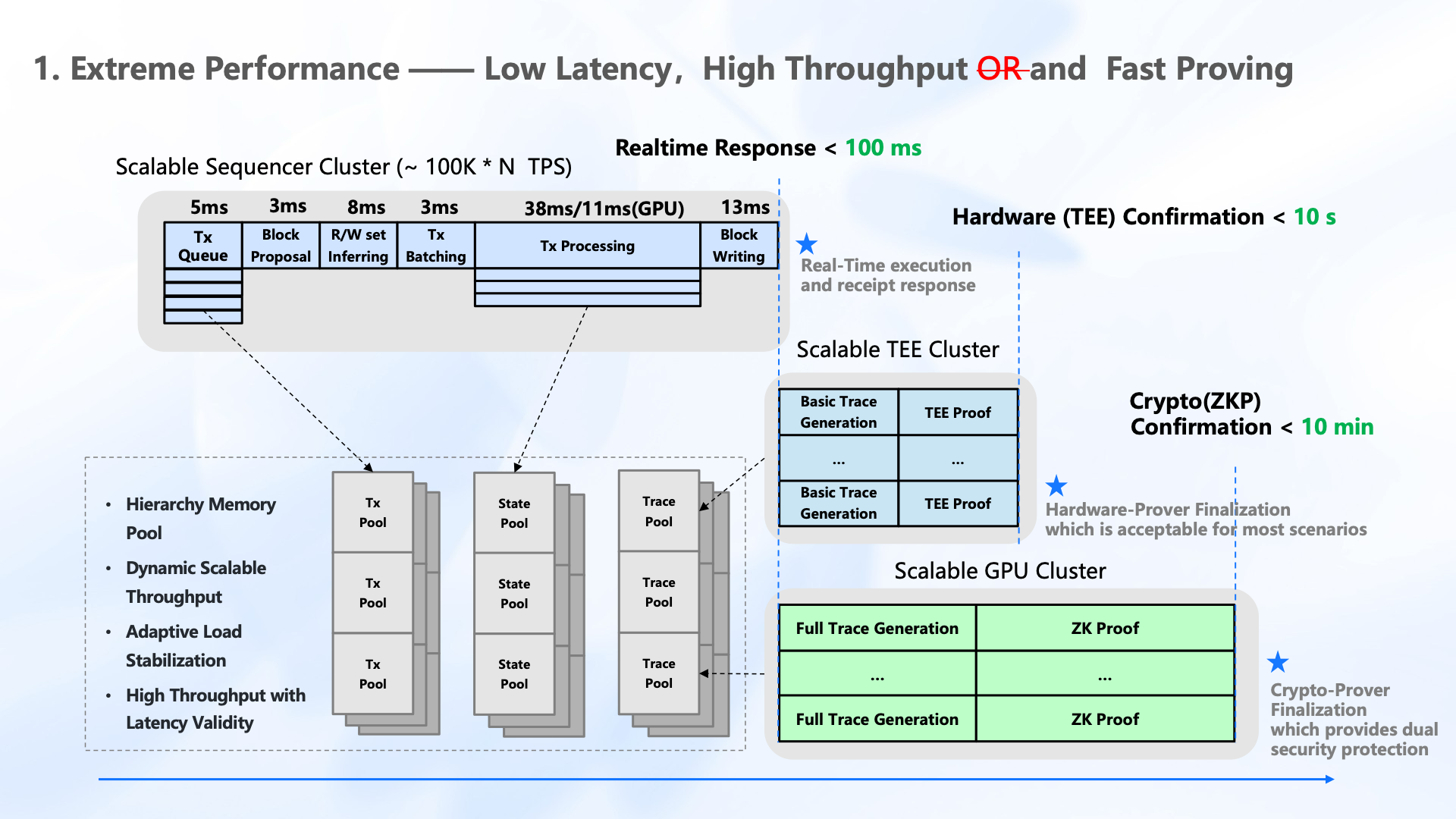
Figure 1: Three-Stage Confirmation Mechanism
To balance throughput and latency, Jovay introduces a three-stage confirmation mechanism, as illustrated in Figure 1:
- Real-Time Execution and Receipt Return: This stage covers block generation, transaction execution, state commitment, and returning receipt to client. Leveraging fully pipelined execution, lazy Just-In-Time (JIT) smart contract compilation, parallel execution engine, and batched data access mechanism, Jovay achieves full process parallelism of computation and I/O. It delivers sub 100ms transaction finality, enabling millisecond level responsiveness for users.
- TEE-Based Hardware Prover Finality: At this stage, a TEE-based proof system generates verifiable attestations for previous execution results, with raw transactions recorded on-chain. Benefiting from the superior scalability of Jovay along with the high performance of TEE, proof generation and verification can be completed within merely 1 second, not accounting for the time required to record raw transactions on Layer 1.
- ZKP-Based Cryptographic Prover Finality: A general-purpose zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) system generates cryptographic proofs for the execution results of Stage 1. Utilizing a random aggregation-based SumCheck algorithm and hardware acceleration, this stage achieves end-to-end finality within 10 minutes, providing global, dual-prover confirmation. The efficiency of this process is several times greater than that of existing implementations, thereby significantly reducing the costs associated with proof generation and verification in Jovay.
3.3.Scalable Subsystem
Jovay comprises the following subsystems:
- Sequencer Subsystem: Handles Layer 2 transaction execution, block generation, and receipt return. It completes real-time transaction result delivery in Stage 1.
- Tracer Subsystem: Generates trace data for the dual-prover system, including Basic Trace to the TEE proof system and Full Trace to the ZKP proof system.
- Bridge Subsystem: Handles raw transaction packaging to DA, proof submission to Layer 1, and cross-chain operations such as Layer 1 deposits, Layer 2 withdrawals and escape hatch functions.
- Prover Subsystem: Produces execution correctness proofs, encompassing both TEE-based hardware proofs and ZKP-based cryptographic proofs.
- Data Storage Subsystem: Provides foundational storage service for other subsystems: zkTrie and KV block storage for Sequencer, TracerDB for Tracer, and Rawtxns storage for the Bridge subsystem.
Notably, Jovay enables elastic scalability, allowing sequencer, tracer, and prover subsystems to be upgraded and expanded independently, for both scaling up and scaling out with diverse demands.
3.4.Full-Cycle Transaction Processing
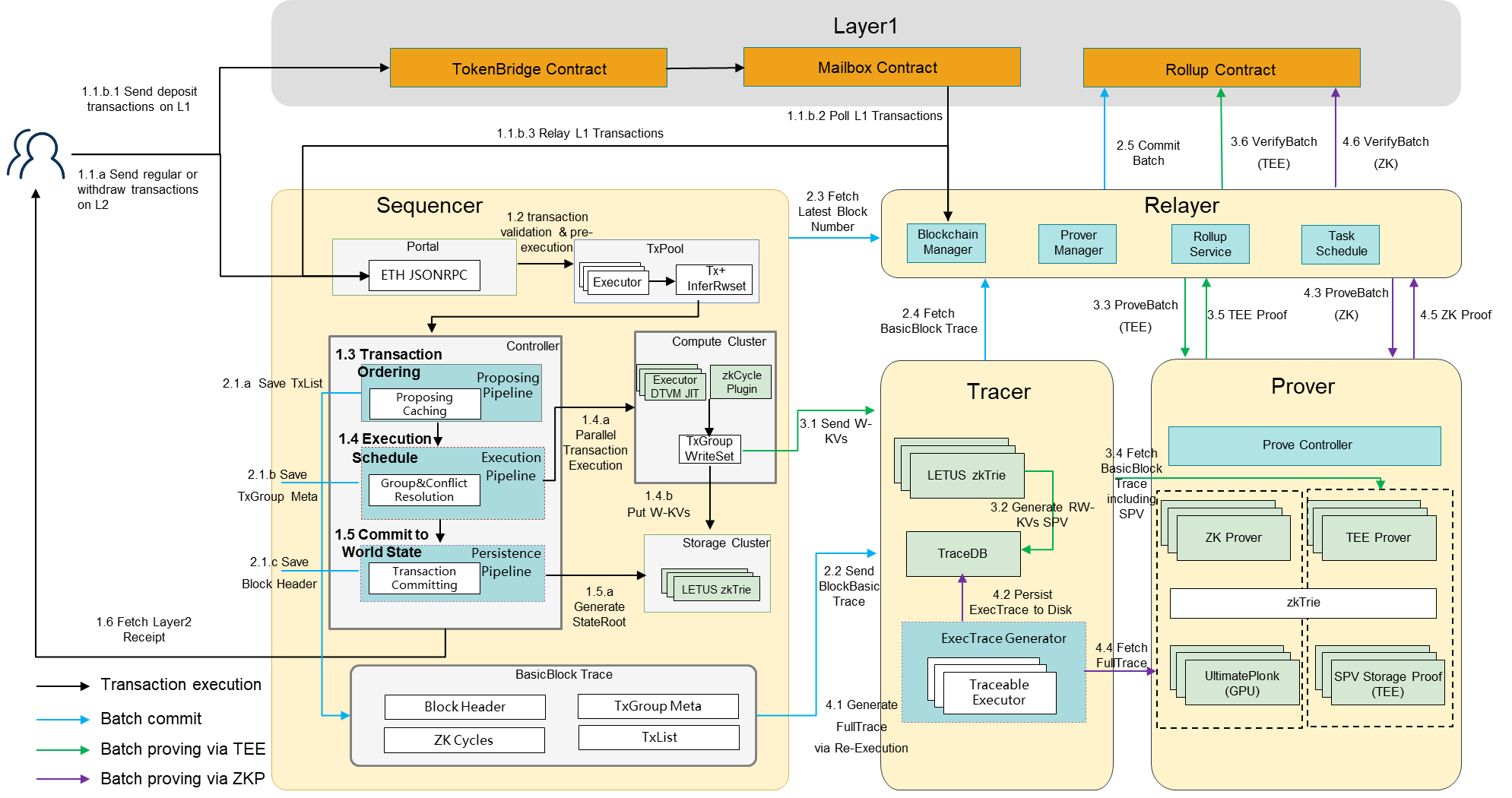
Figure 2: Transaction Processing
As depicted in Figure 2, the full-cycle transaction processing in Jovay consists of four stages: transaction execution, batch commit, batch proof based on trusted hardware, and batch proof based on zero knowledge. Collectively, these stages constitute a complete pipeline from transaction submission to final verification on Layer 1.
- Transaction Execution: Transactions in Jovay can be initiated by users on Layer 2 or triggered by Layer 1 (e.g., deposit transactions captured by the Relayer and forwarded to Layer 2). These transactions pass through the Portal and TxPool, where a pre-execution phase derives their read-write sets. Every 10 milliseconds, the pipeline scheduler batches these transactions, constructs Layer 2 blocks, and forwards them into the execution pipeline. Within this pipeline, transactions are grouped based on read-write conflicts to ensure isolation and are dispatched to computing clusters for parallel execution. Upon completion of each group's execution, the resulting state updates and receipts are written to the storage cluster. Once all groups have been processed, the State Root is calculated, and the block header and body are generated and persistently stored. After this persistence is completed, transaction and receipt information can be queried through the ETH JSON-RPC interface.
- Batch Commit: Each stage of the pipeline generates components of the Basic Trace, which includes transaction grouping information, block header, circuit size, and transaction list. The Sequencer transmits this data to the Tracer, where it is stored in TraceDB. The Relayer monitors newly finalized Layer 2 blocks and incrementally retrieves their Basic Trace. Once a sufficient number of blocks have been collected, they are assembled into a Chunk or Batch and stored locally. Subsequently, a CommitBatch transaction is submitted to the Layer 1 Rollup contract. This ensures data availability on Layer 1 and facilitates subsequent verification processes.
- Batch Proof Based on Trusted Hardware: The Tracer generates SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) data directly from the read-write sets of each block without necessitating re-execution. The Prover retrieves the corresponding Basic Trace and SPV data, then schedules the TEE Prover cluster to re-execute the transactions within a trusted execution environment (TEE). During this process, a partial world state tree is constructed in memory based on the SPV data. Upon completion of the execution, a new block header is generated within the TEE and compared with the original block header from the trace. If the comparison is successful, the Prover generates a hardware signature to attest to the correctness of the execution, which is subsequently persisted. The Relayer periodically checks for new signatures and submits a VerityBatch(TEE) transaction to the Layer 1 Rollup contract. This contract verifies the result using the TEE signature to ensure authenticity.
- Batch Proof Based on Zero Knowledge Proof: The Tracer re-executes each block to generate a Full Trace, utilizing transaction groupings from the BasicBlock Trace to enable parallel execution of transactions without read-write conflicts. Once the execution is complete, the Full Trace is stored in TraceDB. When a batch is formed, the Relayer notifies the Prover, who retrieves the necessary Full Trace and SPV data, and schedules the ZK Prover cluster to perform circuit verification. This process results in the generation and persistence of the zero-knowledge proof. Subsequently, the Relayer retrieves the proof and submits a VerityBatch(ZKP) transaction to the Layer 1 Rollup contract. This contract validates the proof to confirm the correctness of the execution.
4.Extension and Application
4.1.VEPT Verifiable Computation Paradigm
Empowered by LLM technology, AI agents improve decision-making and collaboration efficiency, surpassing traditional software robots. In the Web3 ecosystem, decentralized technologies and token mechanisms have spurred innovation, leading to numerous Web3 + AI projects and open-source initiatives. In scenarios such as encrypted transactions, wallet management, DeFi, and investment research, persistent challenges remain, including private key security, verifiable agent execution, data privacy, scalability, and hosting reliability.
To address the above challenges, VEPT (Verifiable, Extensible, Pluggable, Trusted) framework based on TEE is proposed, as shown in Figure 3. As a new paradigm for Web3 verifiable computing, VEPT enables the integration of blockchain with emerging technologies and applications, allowing AI agents to seamlessly interact with Layer1 and Layer2 blockchain networks through trusted and verifiable extensions. This framework supports Web3 innovation, driving the growth of the blockchain + AI ecosystem. By enhancing security and scalability, VEPT advances decentralized applications and economic development in the Web3 era:
- Verifiable: On-chain and off-chain AI-interoperability protocols and interfaces are standardized. All trusted collaterals are recorded and verified on-chain, extending the trust to blockchain, thereby guaranteeing transparency and verifiability at every step.
- Extensible: VEPT extends multiple capabilities (e.g., trusted big data computation, machine learning, LLMs, and zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs). These functionalities are provided to developers through standardized interfaces. Within this scalable framework, trusted applications deployed on VEPT can also expose their capabilities to a broader developer community.
- Pluggable: The plug-in pattern enables seamless and efficient migration of web3 AI agents, promoting third-party integration and ensuring ecosystem compatibility across diverse domains, including L1/L2 blockchain networks, agent frameworks, decentralized applications (DApps), and multi-agent systems.
- Trusted: From the hardware layer to the foundational service layer and subsequently to the application layer, a hierarchical verification mechanism is implemented across modules to establish an end-to-end chain of trust.
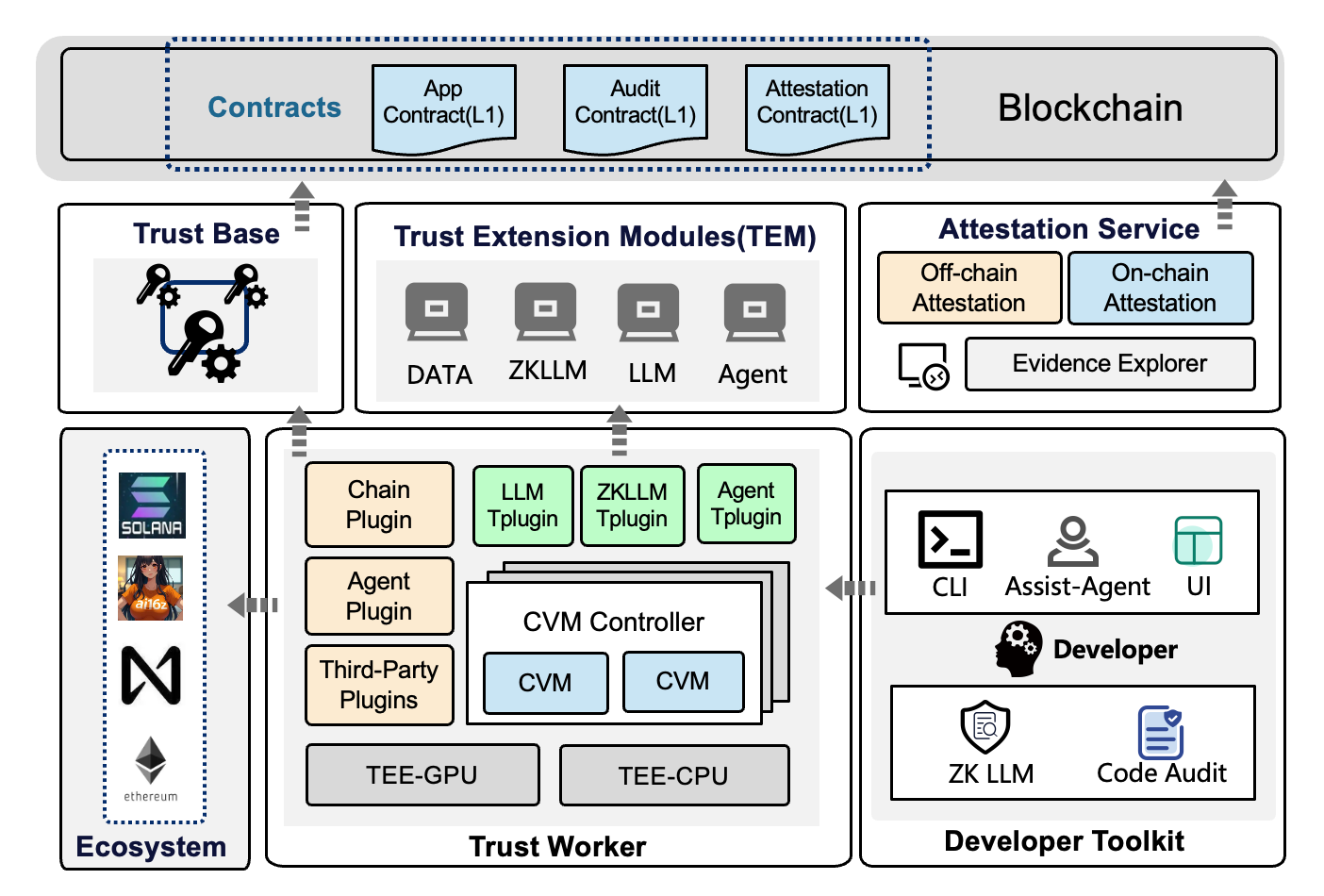
Figure 3: VEPT Architecture
4.2.AI Extended Application
Within the VEPT paradigm, trusted and verifiable computational capabilities are built in Jovay's Layer 2 network. By implementing a set of trusted interoperability protocols, the virtual machine deployed on the Sequencer extends a suite of secure Host APIs, which enable smart contracts to comprehensively encapsulate and manage critical logic such as agent invocation (see Figure 4). This architecture ultimately facilitates the deployment of B-Agent on the blockchain. Throughout its execution, all on-chain and off-chain interactions ranging from chain-of-thought reasoning to memory management are captured as verifiable traces. These traces are subsequently replayed and validated within the proving system to ensure the integrity and correctness of the execution process. By harnessing Jovay's native functionalities, the agent's operational framework supports multiple modes of interaction, delivering tailored and precise services across diverse application scenarios.
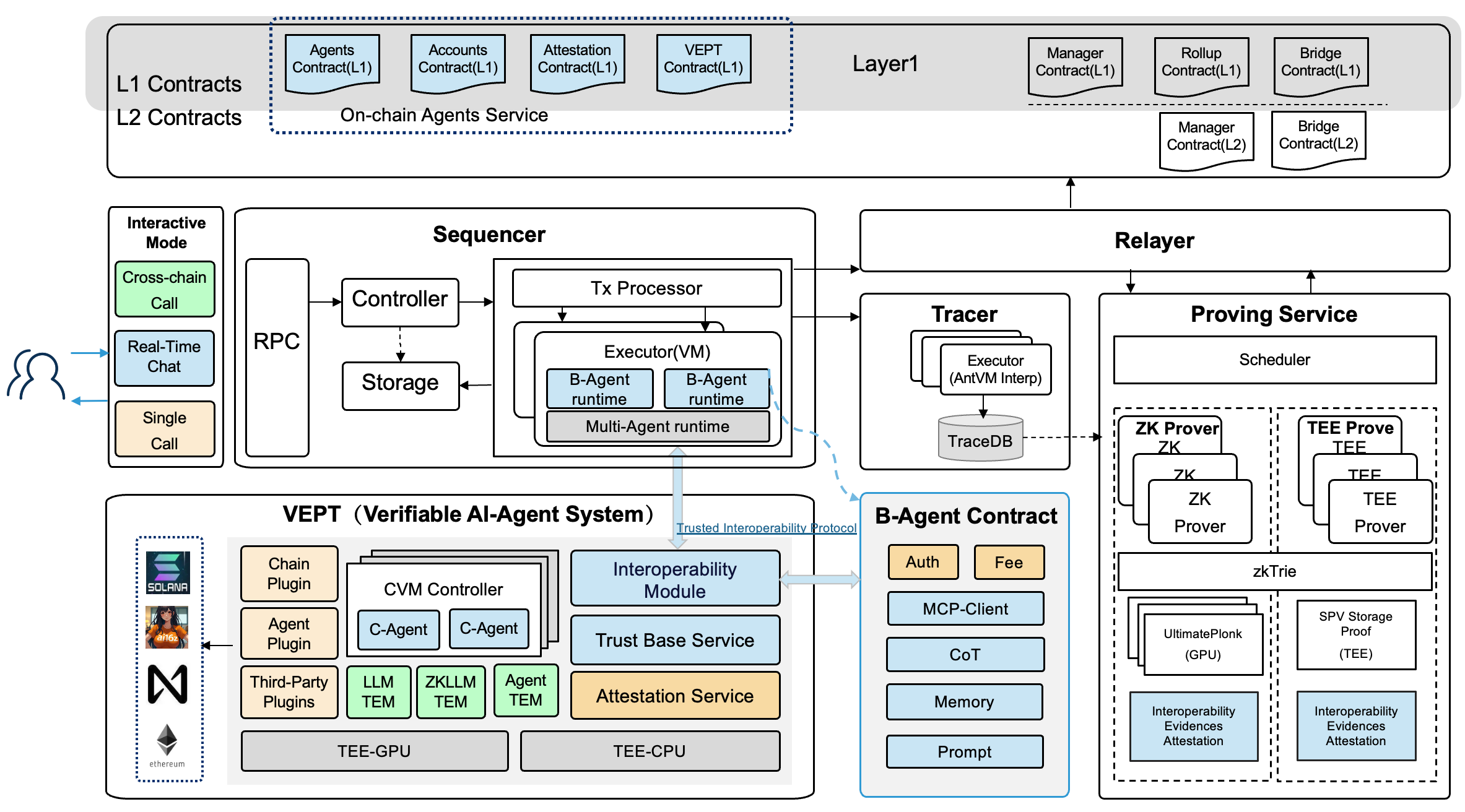
Figure 4: AI Extension Architecture Based on VEPT
5.Conclusion
The evolution of blockchain technology has undergone continuous advancement, with Layer 2 representing a pivotal milestone in this journey. Jovay has redefined the possibility of expansion through technological innovation and provided infrastructure support for the large-scale application of Web3. We firmly believe that Jovay is not only a technical solution, but also a bridge to an open, efficient and decentralized future. With the prosperity and evolution of the ecosystem, Jovay will work with global partners to jointly write a new chapter in blockchain technology and industry ecology. We hope Jovay can work with you to "Tokenize the Future, Chain the Value".
References
[1] The multi-prover scheme. https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/a-simple-l2-security-and-finalization-roadmap/23309, 2025.