Create and Deploy Your First Token
This guide walks you through the process of building and deploying an ERC-20 token on Jovay, a fully Ethereum-compatible blockchain. If you're already familiar with using Foundry to develop smart contracts, you'll feel right at home — Just write, build, and deploy like you always do. New to Foundry? No problem. This document follows standard Foundry practices and includes all the steps you need to get started with confidence.
By the end, you’ll have:
- A working token contract
- Experience deploying and verifying smart contracts
- The skills to interact with your token programmatically
Before you begin, please note the connection details for the network you are targeting:
| Network | RPC URL | Chain ID |
|---|---|---|
| Jovay Mainnet | https://rpc.jovay.io | 5734951 |
| Jovay Testnet | https://api.zan.top/public/jovay-testnet | 2019775 |
This guide will use the Testnet configuration in its examples.
🧰 Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have:
- Have Foundry Installed – Foundry
- Have an account with funds – You can get DEV tokens for testing on Jovay once every 24 hours from the Faucet
- Access to Jovay Devnet or Testnet – To deploy and interact with your token, you will need to have your own endpoint and API key, which you can get from one of the supported QuickStart
Step 1: Set Up Your Project
Clone the example repository:
bashwget 'https://web3-static-prod.oss-ap-southeast-1.aliyuncs.com/static/Jovay/JovayExamples.tar.gz' tar -xvzf JovayExamples.tar.gz cd JovayExamples/foundry/ERC20Example/Install OpenZeppelin Contracts:
Foundry uses forge to manage dependencies. Install OpenZeppelin required by the examples:
bashforge install OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-contracts --no-git
Step 2: Configure Your Environment
Before writing the contract, it's best to set up your deployment environment.
1. (Optional) Generate a Private Key
To deploy contracts, you need a wallet with a private key. If you don't have one, you can generate a new one using ethers.js.
First, install ethers.js in a temporary directory:
npm i ethersNext, create and run a gen_eth_key.js script to get a new keypair.
const { ethers } = require('ethers');
const wallet = ethers.Wallet.createRandom();
console.log('Private Key:', wallet.privateKey);
console.log('Address :', wallet.address);Run the script:
node gen_eth_key.jsThe output will give you a new Private Key and Address. Save these securely. You will use the Private Key in the next step. Remember to also send some testnet funds to the new Address using the Jovay Faucet.
2. Set Environment Variables
Foundry scripts read configuration like private keys and RPC URLs from environment variables. You can set them in your shell for the current session.
For Testnet (as used in this guide's examples):
export PRIVATE_KEY="YOUR_TESTNET_WALLET_PRIVATE_KEY"
export RPC_URL="https://api.zan.top/public/jovay-testnet"For Mainnet:
export PRIVATE_KEY="YOUR_MAINNET_WALLET_PRIVATE_KEY"
export RPC_URL="https://rpc.jovay.io"Tip: For a more permanent solution, you can add these
exportlines to your shell's profile file (e.g.,.bashrc,.zshrc) or save them in a.envfile and runsource .envin your terminal before you start working.
Step 3: Write the Token Contract
Create a New Solidity File:
bashtouch src/MyToken.solPaste the following code into
src/MyToken.sol:solidity// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.0; import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol"; contract MyToken is ERC20 { constructor(uint256 initialSupply) ERC20("MyToken", "MTK") { _mint(msg.sender, initialSupply); } function decimals() public pure override returns (uint8) { return 6; } }Compile the Smart Contract:
bashforge buildTest the Smart Contract (optional but recommended):
bashtouch test/MyToken.t.solPaste the following code into
test/MyToken.t.sol:solidity// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.0; import "forge-std/Test.sol"; import "../src/MyToken.sol"; contract MyTokenTest is Test { MyToken public token; address public owner = address(0x1); address public alice = address(0x2); function setUp() public { vm.prank(owner); token = new MyToken(1_000_000e6); // initial supply with 6 decimals } // Test name and symbol function testNameAndSymbol() public view { assertEq(token.name(), "MyToken"); assertEq(token.symbol(), "MTK"); } // Test initial supply function testInitialSupply() public view { assertEq(token.balanceOf(owner), 1_000_000e6); } // Test decimals are 6 function testDecimals() public view { assertEq(token.decimals(), 6); } // Test token transfer function testTransfer() public { vm.startPrank(owner); uint256 sendAmount = 100e6; // 100 tokens uint256 ownerBalanceBefore = token.balanceOf(owner); uint256 aliceBalanceBefore = token.balanceOf(alice); token.transfer(alice, sendAmount); uint256 ownerBalanceAfter = token.balanceOf(owner); uint256 aliceBalanceAfter = token.balanceOf(alice); assertEq(ownerBalanceAfter, ownerBalanceBefore - sendAmount); assertEq(aliceBalanceAfter, aliceBalanceBefore + sendAmount); vm.stopPrank(); } // Test transfer reverts when balance is insufficient function testTransferRevertsWhenInsufficientBalance() public { vm.expectRevert(); token.transfer(alice, 1_000_001e6); // Attempt to send more than balance } }Test it:
bashforge test
Step 4: Deploy the Token Contract
Create a Deployment Script:
bashtouch script/DeployToken.s.solPaste the following code into
script/DeployToken.s.sol:solidity// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.0; import "forge-std/Script.sol"; import "../src/MyToken.sol"; contract DeployToken is Script { function run() external { uint256 deployerPrivateKey = vm.envUint("PRIVATE_KEY"); vm.startBroadcast(deployerPrivateKey); MyToken token = new MyToken(1000000); vm.stopBroadcast(); } }Deploy the contract:
bashforge script script/DeployToken.s.sol --rpc-url $RPC_URL --broadcastIf your script's execution succeeds, your terminal should resemble the output below:
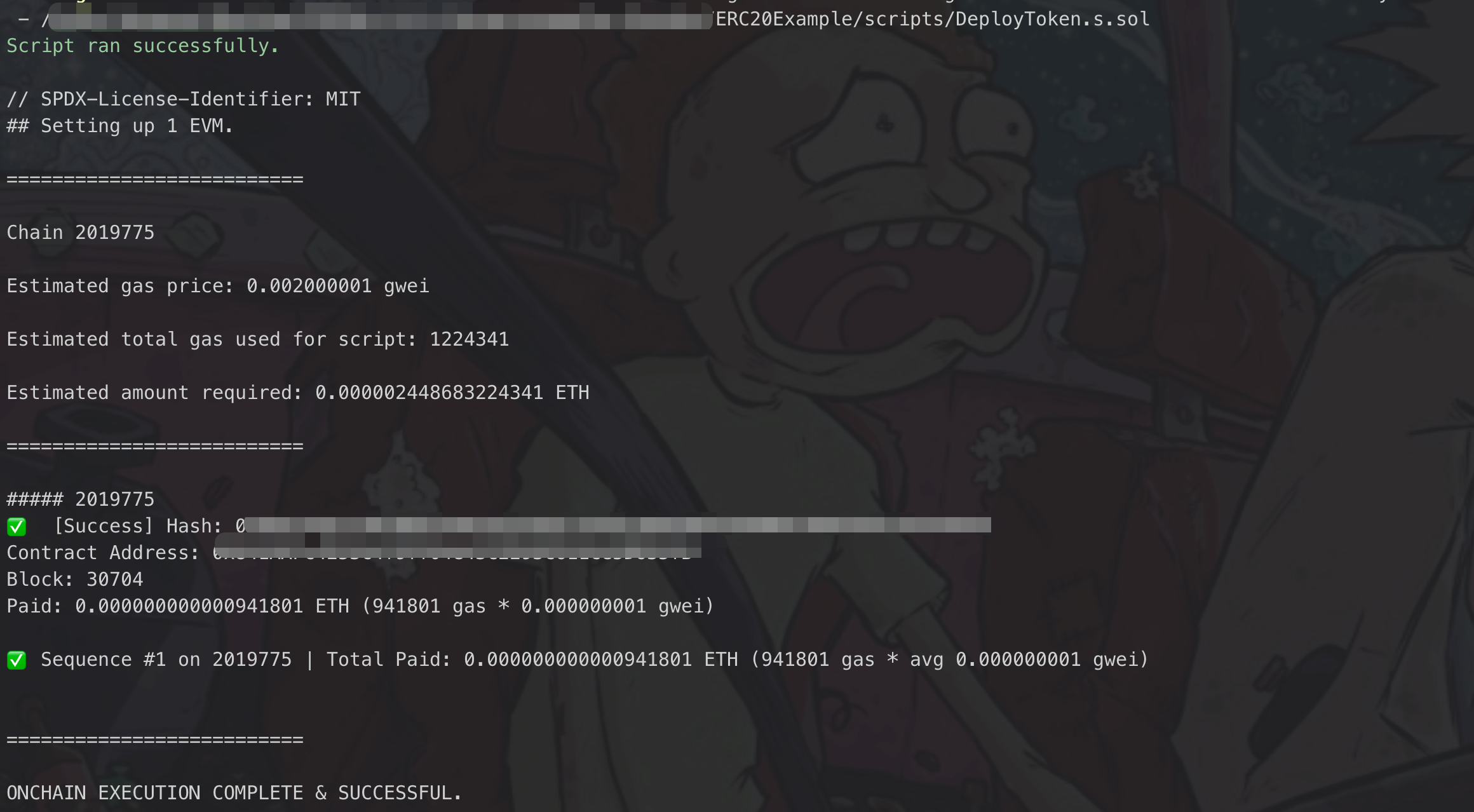
Step 5: Interact with the Token Contract
Create a script:
bashtouch script/InteractToken.s.solPaste the following code into
script/InteractToken.s.sol:solidity// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.13; import {Script, console} from "forge-std/Script.sol"; import {MyToken} from "../src/MyToken.sol"; contract InteractToken is Script { function run() external { uint256 deployerPrivateKey = vm.envUint("PRIVATE_KEY"); vm.startBroadcast(deployerPrivateKey); MyToken token = MyToken(address(0x00)); // Check balance uint256 balance = token.balanceOf(msg.sender); console.log("Balance:", balance); // Transfer tokens token.transfer(address(0x00), 1); console.log("Tokens transferred"); vm.stopBroadcast(); } }Note: Remember to replace with your token contract address, recipient address and amount.
Execute the script:
bashforge script script/InteractToken.s.sol --rpc-url $RPC_URL --broadcastIf your script's execution succeeds, your terminal should resemble the output below:
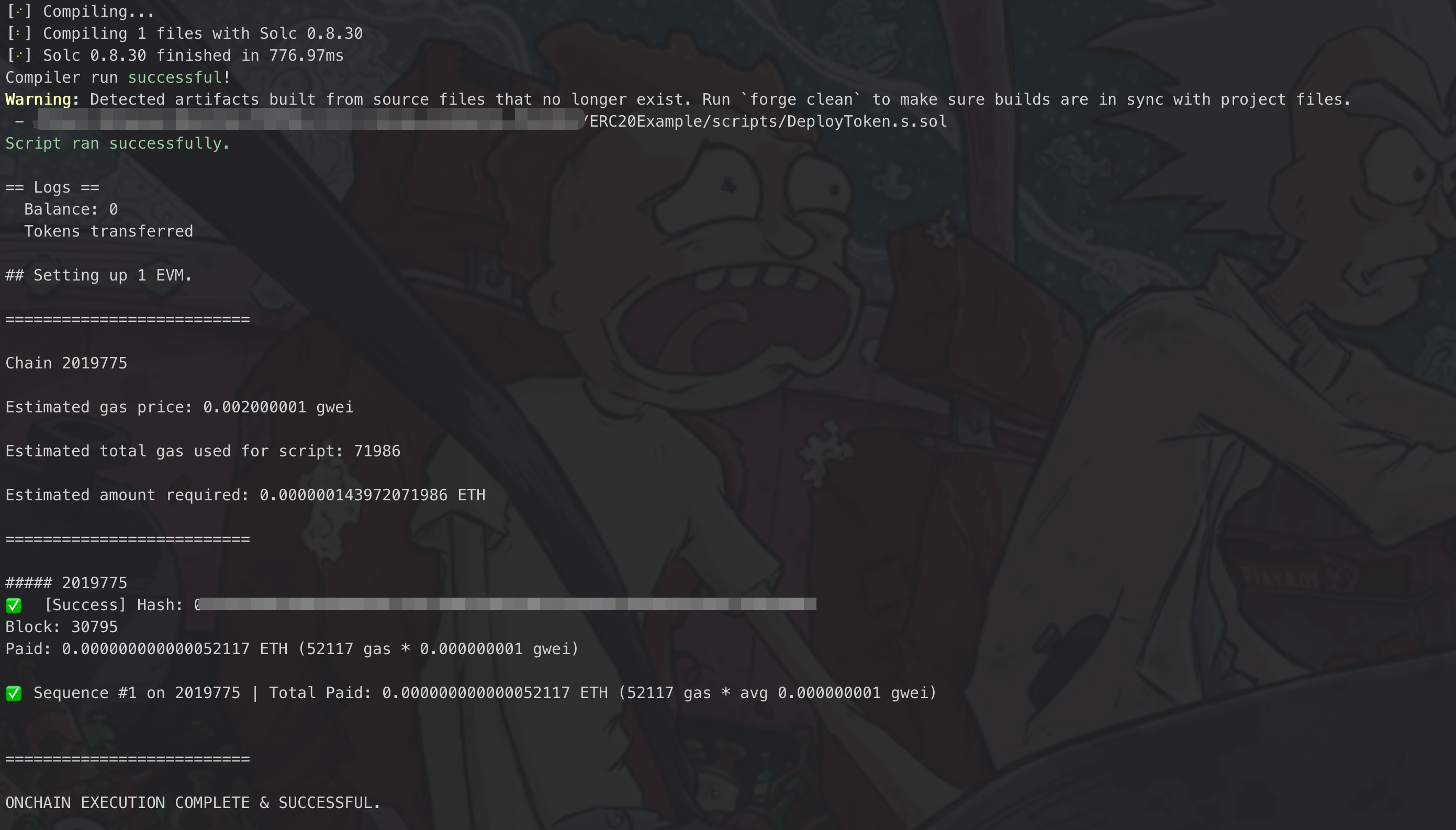
❓ Troubleshooting Tips
- Deployment fails? Make sure your wallet has enough testnet tokens.
- Can't interact with the contract? Double-check the contract address and ABI.
- Transfer fails? Confirm your wallet has enough balance.
✅ Conclusion
You’ve just built, deployed, and verified your first token on the Jovay blockchain using Foundry! This process covers the basics of smart contract development, deployment, and verification — essential skills for any Web3 developer.
If you run into issues, refer back to this guide or check out the official Foundry documentation.
Happy coding! 🚀